QTransform¶
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def __add__ (, n)
- def __div__ (, n)
- def __eq__ (arg__1)
- def __iadd__ (div)
- def __idiv__ (div)
- def __imul__ (arg__1)
- def __imul__ (div)
- def __isub__ (div)
- def __mul__ (, n)
- def __mul__ (o)
- def __ne__ (arg__1)
- def __reduce__ ()
- def __repr__ ()
- def __sub__ (, n)
- def adjoint ()
- def det ()
- def determinant ()
- def dx ()
- def dy ()
- def inline_type ()
- def inverted ()
- def isAffine ()
- def isIdentity ()
- def isInvertible ()
- def isRotating ()
- def isScaling ()
- def isTranslating ()
- def m11 ()
- def m12 ()
- def m13 ()
- def m21 ()
- def m22 ()
- def m23 ()
- def m31 ()
- def m32 ()
- def m33 ()
- def map (a)
- def map (a)
- def map (l)
- def map (l)
- def map (p)
- def map (p)
- def map (p)
- def map (r)
- def map (x, y)
- def mapRect (arg__1)
- def mapRect (arg__1)
- def mapToPolygon (r)
- def quadToQuad (arg__1, arg__2)
- def quadToSquare (arg__1)
- def reset ()
- def rotate (a[, axis=Qt.ZAxis])
- def rotateRadians (a[, axis=Qt.ZAxis])
- def scale (sx, sy)
- def setMatrix (m11, m12, m13, m21, m22, m23, m31, m32, m33)
- def shear (sh, sv)
- def squareToQuad (arg__1)
- def toAffine ()
- def translate (dx, dy)
- def transposed ()
- def type ()
Static functions¶
- def fromScale (dx, dy)
- def fromTranslate (dx, dy)
- def quadToQuad (one, two, result)
- def quadToSquare (quad, result)
- def squareToQuad (square, result)
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtGui.QTransform class specifies 2D transformations of a coordinate system.
A transformation specifies how to translate, scale, shear, rotate or project the coordinate system, and is typically used when rendering graphics.
PySide.QtGui.QTransform differs from PySide.QtGui.QMatrix in that it is a true 3x3 matrix, allowing perspective transformations. PySide.QtGui.QTransform ‘s PySide.QtGui.QTransform.toAffine() method allows casting PySide.QtGui.QTransform to PySide.QtGui.QMatrix . If a perspective transformation has been specified on the matrix, then the conversion will cause loss of data.
PySide.QtGui.QTransform is the recommended transformation class in Qt.
A PySide.QtGui.QTransform object can be built using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.setMatrix() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.rotate() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear() functions. Alternatively, it can be built by applying basic matrix operations . The matrix can also be defined when constructed, and it can be reset to the identity matrix (the default) using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.reset() function.
The PySide.QtGui.QTransform class supports mapping of graphic primitives: A given point, line, polygon, region, or painter path can be mapped to the coordinate system defined by this matrix using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map() function. In case of a rectangle, its coordinates can be transformed using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapRect() function. A rectangle can also be transformed into a polygon (mapped to the coordinate system defined by this matrix), using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapToPolygon() function.
PySide.QtGui.QTransform provides the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isIdentity() function which returns true if the matrix is the identity matrix, and the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isInvertible() function which returns true if the matrix is non-singular (i.e. AB = BA = I). The PySide.QtGui.QTransform.inverted() function returns an inverted copy of this matrix if it is invertible (otherwise it returns the identity matrix), and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.adjoint() returns the matrix’s classical adjoint. In addition, PySide.QtGui.QTransform provides the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.determinant() function which returns the matrix’s determinant.
Finally, the PySide.QtGui.QTransform class supports matrix multiplication, addition and subtraction, and objects of the class can be streamed as well as compared.
Rendering Graphics¶
When rendering graphics, the matrix defines the transformations but the actual transformation is performed by the drawing routines in PySide.QtGui.QPainter .
By default, PySide.QtGui.QPainter operates on the associated device’s own coordinate system. The standard coordinate system of a PySide.QtGui.QPaintDevice has its origin located at the top-left position. The x values increase to the right; y values increase downward. For a complete description, see the coordinate system documentation.
PySide.QtGui.QPainter has functions to translate, scale, shear and rotate the coordinate system without using a PySide.QtGui.QTransform . For example:
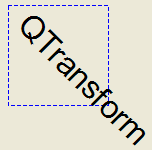
def paintEvent(self, event) painter = QPainter(self) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue, 1, Qt.DashLine)) painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100) painter.rotate(45) painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24)) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.black, 1)) painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform")Although these functions are very convenient, it can be more efficient to build a PySide.QtGui.QTransform and call QPainter.setTransform() if you want to perform more than a single transform operation. For example:
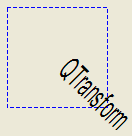
def paintEvent(self, event) painter = QPainter(self) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue, 1, Qt.DashLine)) painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100) transform = QTransform() transform.translate(50, 50) transform.rotate(45) transform.scale(0.5, 1.0) painter.setTransform(transform) painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24)) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.black, 1)) painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform")
Basic Matrix Operations¶
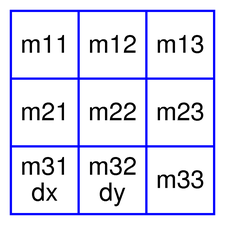
A PySide.QtGui.QTransform object contains a 3 x 3 matrix. The m31 (dx ) and m32 (dy ) elements specify horizontal and vertical translation. The m11 and m22 elements specify horizontal and vertical scaling. The m21 and m12 elements specify horizontal and vertical shearing . And finally, the m13 and m23 elements specify horizontal and vertical projection, with m33 as an additional projection factor.
PySide.QtGui.QTransform transforms a point in the plane to another point using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy if is not affine: w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33 x' /= w' y' /= w'The point (x, y) is the original point, and (x’, y’) is the transformed point. (x’, y’) can be transformed back to (x, y) by performing the same operation on the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.inverted() matrix.
The various matrix elements can be set when constructing the matrix, or by using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.setMatrix() function later on. They can also be manipulated using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.rotate() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale() and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear() convenience functions. The currently set values can be retrieved using the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m11() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m12() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m13() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m21() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m22() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m23() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m31() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m32() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m33() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dx() and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dy() functions.
Translation is the simplest transformation. Setting dx and dy will move the coordinate system dx units along the X axis and dy units along the Y axis. Scaling can be done by setting m11 and m22 . For example, setting m11 to 2 and m22 to 1.5 will double the height and increase the width by 50%. The identity matrix has m11 , m22 , and m33 set to 1 (all others are set to 0) mapping a point to itself. Shearing is controlled by m12 and m21 . Setting these elements to values different from zero will twist the coordinate system. Rotation is achieved by setting both the shearing factors and the scaling factors. Perspective transformation is achieved by setting both the projection factors and the scaling factors.
Here’s the combined transformations example using basic matrix operations:
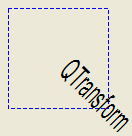
def paintEvent(self, event) pi = 3.14 a = pi/180 * 45.0 sina = sin(a) cosa = cos(a) translationTransform = QTransform(1, 0, 0, 1, 50.0, 50.0) rotationTransform = QTransform(cosa, sina, -sina, cosa, 0, 0) scalingTransform = QTransform(0.5, 0, 0, 1.0, 0, 0) transform = QTransform() transform = scalingTransform * rotationTransform * translationTransform painter = QPainter(self) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.blue, 1, Qt.DashLine)) painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100) painter.setTransform(transform) painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24)) painter.setPen(QPen(Qt.black, 1)) painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform")See also
PySide.QtGui.QPainter Coordinate System Affine Transformations Demo Transformations Example
- class PySide.QtGui.QTransform¶
- class PySide.QtGui.QTransform(mtx)
- class PySide.QtGui.QTransform(QTransform)
- class PySide.QtGui.QTransform(h11, h12, h13, h21, h22, h23, h31, h32[, h33=1.0])
- class PySide.QtGui.QTransform(h11, h12, h21, h22, dx, dy)
Parameters: - h31 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h21 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h32 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h11 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h22 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h33 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h12 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h23 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- dx – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- h13 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- dy – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- mtx – PySide.QtGui.QMatrix
- QTransform – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
Constructs an identity matrix.
All elements are set to zero except m11 and m22 (specifying the scale) and m13 which are set to 1.
See also
Constructs a matrix that is a copy of the given matrix . Note that the m13 , m23 , and m33 elements are set to 0, 0, and 1 respectively.
Constructs a matrix with the elements, m11 , m12 , m13 , m21 , m22 , m23 , m31 , m32 , m33 .
See also
Constructs a matrix with the elements, m11 , m12 , m21 , m22 , dx and dy .
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.TransformationType¶
Constant Description QTransform.TxNone QTransform.TxTranslate QTransform.TxScale QTransform.TxRotate QTransform.TxShear QTransform.TxProject
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__reduce__()¶
Return type: PyObject
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__repr__()¶
Return type: PyObject
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.adjoint()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform Returns the adjoint of this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.det()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the matrix’s determinant. Use PySide.QtGui.QTransform.determinant() instead.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.determinant()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the matrix’s determinant.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dx()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the horizontal translation factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m31() PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dy()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the vertical translation factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- static PySide.QtGui.QTransform.fromScale(dx, dy)¶
Parameters: - dx – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- dy – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Return type: Creates a matrix which corresponds to a scaling of sx horizontally and sy vertically. This is the same as PySide.QtGui.QTransform.QTransform() .scale(sx, sy) but slightly faster.
- static PySide.QtGui.QTransform.fromTranslate(dx, dy)¶
Parameters: - dx – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- dy – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Return type: Creates a matrix which corresponds to a translation of dx along the x axis and dy along the y axis. This is the same as PySide.QtGui.QTransform.QTransform() .translate(dx, dy) but slightly faster.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.inline_type()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform.TransformationType
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.inverted()¶
Return type: PyTuple Returns an inverted copy of this matrix.
If the matrix is singular (not invertible), the returned matrix is the identity matrix. If invertible is valid (i.e. not 0), its value is set to true if the matrix is invertible, otherwise it is set to false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isAffine()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix represent an affine transformation, otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isIdentity()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix is the identity matrix, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isInvertible()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix is invertible, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isRotating()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix represents some kind of a rotating transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isScaling()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix represents a scaling transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isTranslating()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if the matrix represents a translating transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m11()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the horizontal scaling factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m12()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the vertical shearing factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m13()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the horizontal projection factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m21()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the horizontal shearing factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m22()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the vertical scaling factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m23()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the vertical projection factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m31()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the horizontal translation factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dx() PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m32()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the vertical translation factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.dy() PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.m33()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.qreal Returns the division factor.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(r)¶
Parameters: r – PySide.QtGui.QRegion Return type: PySide.QtGui.QRegion This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtGui.QRegion object that is a copy of the given region , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
Calling this method can be rather expensive if rotations or shearing are used.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(x, y)
Parameters: - x – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- y – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Maps the given coordinates x and y into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. The resulting values are put in *``tx`` and *``ty`` , respectively.
The coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy if is not affine: w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33 x' /= w' y' /= w'The point (x, y) is the original point, and (x’, y’) is the transformed point.
See also
Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(a)
Parameters: a – PySide.QtGui.QPolygon Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPolygon This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtGui.QPolygon object that is a copy of the given polygon , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(a)
Parameters: a – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF object that is a copy of the given polygon , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(l)
Parameters: l – PySide.QtCore.QLine Return type: PySide.QtCore.QLine This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QLineF object that is a copy of the given line, l , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(l)
Parameters: l – PySide.QtCore.QLineF Return type: PySide.QtCore.QLineF This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QLine object that is a copy of the given line , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(p)
Parameters: p – PySide.QtCore.QPointF Return type: PySide.QtCore.QPointF This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QPointF object that is a copy of the given point, p , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(p)
Parameters: p – PySide.QtGui.QPainterPath Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPainterPath This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtGui.QPainterPath object that is a copy of the given path , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.map(p)
Parameters: p – PySide.QtCore.QPoint Return type: PySide.QtCore.QPoint This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QPoint object that is a copy of the given point , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapRect(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.QRectF Return type: PySide.QtCore.QRectF Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QRectF object that is a copy of the given rectangle , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
The rectangle’s coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy if is not affine: w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33 x' /= w' y' /= w'If rotation or shearing has been specified, this function returns the bounding rectangle. To retrieve the exact region the given rectangle maps to, use the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapToPolygon() function instead.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapToPolygon() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapRect(arg__1)
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtCore.QRect Return type: PySide.QtCore.QRect This is an overloaded function.
Creates and returns a PySide.QtCore.QRect object that is a copy of the given rectangle , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapToPolygon(r)¶
Parameters: r – PySide.QtCore.QRect Return type: PySide.QtGui.QPolygon Creates and returns a PySide.QtGui.QPolygon representation of the given rectangle , mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
The rectangle’s coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy if is not affine: w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33 x' /= w' y' /= w'Polygons and rectangles behave slightly differently when transformed (due to integer rounding), so matrix.map(QPolygon(rectangle)) is not always the same as matrix.mapToPolygon(rectangle) .
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.mapRect() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__ne__(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QTransform Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this matrix is not equal to the given matrix , otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__mul__(n)¶
Parameters: n – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__mul__(o)
Parameters: o – PySide.QtGui.QTransform Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform Returns the result of multiplying this matrix by the given matrix .
Note that matrix multiplication is not commutative, i.e. a*b != b*a.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__imul__(div)¶
Parameters: div – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform This is an overloaded function.
Returns the result of performing an element-wise multiplication of this matrix with the given scalar .
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__imul__(arg__1)
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QTransform Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform This is an overloaded function.
Returns the result of multiplying this matrix by the given matrix .
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__add__(n)¶
Parameters: n – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__iadd__(div)¶
Parameters: div – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform This is an overloaded function.
Returns the matrix obtained by adding the given scalar to each element of this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__sub__(n)¶
Parameters: n – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__isub__(div)¶
Parameters: div – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform This is an overloaded function.
Returns the matrix obtained by subtracting the given scalar from each element of this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__div__(n)¶
Parameters: n – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__idiv__(div)¶
Parameters: div – PySide.QtCore.qreal Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform This is an overloaded function.
Returns the result of performing an element-wise division of this matrix by the given scalar .
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.__eq__(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QTransform Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns true if this matrix is equal to the given matrix , otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.quadToQuad(arg__1, arg__2)¶
Parameters: - arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
- arg__2 – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
Return type: PyObject
- static PySide.QtGui.QTransform.quadToQuad(one, two, result)
Parameters: - one – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
- two – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
- result – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Creates a transformation matrix, trans , that maps a four-sided polygon, one , to another four-sided polygon, two . Returns true if the transformation is possible; otherwise returns false.
This is a convenience method combining PySide.QtGui.QTransform.quadToSquare() and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.squareToQuad() methods. It allows the input quad to be transformed into any other quad.
- static PySide.QtGui.QTransform.quadToSquare(quad, result)¶
Parameters: - quad – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
- result – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Creates a transformation matrix, trans , that maps a four-sided polygon, quad , to a unit square. Returns true if the transformation is constructed or false if such a transformation does not exist.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.quadToSquare(arg__1)
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF Return type: PyObject
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.reset()¶
Resets the matrix to an identity matrix, i.e. all elements are set to zero, except m11 and m22 (specifying the scale) and m33 which are set to 1.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.QTransform() PySide.QtGui.QTransform.isIdentity() Basic Matrix Operations
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.rotate(a[, axis=Qt.ZAxis])¶
Parameters: - a – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- axis – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Axis
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.rotateRadians(a[, axis=Qt.ZAxis])¶
Parameters: - a – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- axis – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Axis
Return type:
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale(sx, sy)¶
Parameters: - sx – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- sy – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Return type: Scales the coordinate system by sx horizontally and sy vertically, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.setMatrix(m11, m12, m13, m21, m22, m23, m31, m32, m33)¶
Parameters: - m11 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m12 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m13 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m21 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m22 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m23 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m31 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m32 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- m33 – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Sets the matrix elements to the specified values, m11 , m12 , m13m21 , m22 , m23m31 , m32 and m33 . Note that this function replaces the previous values. PySide.QtGui.QTransform provides the PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.rotate() , PySide.QtGui.QTransform.scale() and PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear() convenience functions to manipulate the various matrix elements based on the currently defined coordinate system.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QTransform.QTransform()
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.shear(sh, sv)¶
Parameters: - sh – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- sv – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Return type: Shears the coordinate system by sh horizontally and sv vertically, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.squareToQuad(arg__1)¶
Parameters: arg__1 – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF Return type: PyObject
- static PySide.QtGui.QTransform.squareToQuad(square, result)
Parameters: - square – PySide.QtGui.QPolygonF
- result – PySide.QtGui.QTransform
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Creates a transformation matrix, trans , that maps a unit square to a four-sided polygon, quad . Returns true if the transformation is constructed or false if such a transformation does not exist.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.toAffine()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMatrix Returns the PySide.QtGui.QTransform as an affine matrix.
Warning
If a perspective transformation has been specified, then the conversion will cause loss of data.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.translate(dx, dy)¶
Parameters: - dx – PySide.QtCore.qreal
- dy – PySide.QtCore.qreal
Return type: Moves the coordinate system dx along the x axis and dy along the y axis, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.transposed()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform Returns the transpose of this matrix.
- PySide.QtGui.QTransform.type()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTransform.TransformationType Returns the transformation type of this matrix.
The transformation type is the highest enumeration value capturing all of the matrix’s transformations. For example, if the matrix both scales and shears, the type would be TxShear , because TxShear has a higher enumeration value than TxScale .
Knowing the transformation type of a matrix is useful for optimization: you can often handle specific types more optimally than handling the generic case.




