QMainWindow¶

Synopsis¶
Functions¶
- def addDockWidget (area, dockwidget)
- def addDockWidget (area, dockwidget, orientation)
- def addToolBar (area, toolbar)
- def addToolBar (title)
- def addToolBar (toolbar)
- def addToolBarBreak ([area=Qt.TopToolBarArea])
- def centralWidget ()
- def corner (corner)
- def dockOptions ()
- def dockWidgetArea (dockwidget)
- def documentMode ()
- def iconSize ()
- def insertToolBar (before, toolbar)
- def insertToolBarBreak (before)
- def isAnimated ()
- def isDockNestingEnabled ()
- def isSeparator (pos)
- def menuBar ()
- def menuWidget ()
- def removeDockWidget (dockwidget)
- def removeToolBar (toolbar)
- def removeToolBarBreak (before)
- def restoreDockWidget (dockwidget)
- def restoreState (state[, version=0])
- def saveState ([version=0])
- def setCentralWidget (widget)
- def setCorner (corner, area)
- def setDockOptions (options)
- def setDocumentMode (enabled)
- def setIconSize (iconSize)
- def setMenuBar (menubar)
- def setMenuWidget (menubar)
- def setStatusBar (statusbar)
- def setTabPosition (areas, tabPosition)
- def setTabShape (tabShape)
- def setToolButtonStyle (toolButtonStyle)
- def setUnifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac (set)
- def splitDockWidget (after, dockwidget, orientation)
- def statusBar ()
- def tabPosition (area)
- def tabShape ()
- def tabifiedDockWidgets (dockwidget)
- def tabifyDockWidget (first, second)
- def toolBarArea (toolbar)
- def toolBarBreak (toolbar)
- def toolButtonStyle ()
- def unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac ()
Virtual functions¶
- def createPopupMenu ()
Slots¶
- def setAnimated (enabled)
- def setDockNestingEnabled (enabled)
Signals¶
- def iconSizeChanged (iconSize)
- def toolButtonStyleChanged (toolButtonStyle)
Detailed Description¶
The PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow class provides a main application window.
Qt Main Window Framework¶
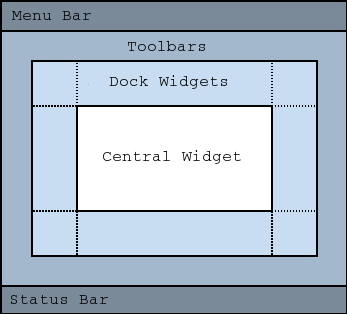
A main window provides a framework for building an application’s user interface. Qt has PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow and its related classes for main window management. PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow has its own layout to which you can add PySide.QtGui.QToolBar s, PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget s, a PySide.QtGui.QMenuBar , and a PySide.QtGui.QStatusBar . The layout has a center area that can be occupied by any kind of widget. You can see an image of the layout below.
Note
Creating a main window without a central widget is not supported. You must have a central widget even if it is just a placeholder.
Creating Main Window Components¶
A central widget will typically be a standard Qt widget such as a PySide.QtGui.QTextEdit or a PySide.QtGui.QGraphicsView . Custom widgets can also be used for advanced applications. You set the central widget with setCentralWidget() .
Main windows have either a single (SDI) or multiple (MDI) document interface. You create MDI applications in Qt by using a PySide.QtGui.QMdiArea as the central widget.
We will now examine each of the other widgets that can be added to a main window. We give examples on how to create and add them.
Creating Toolbars¶
Toolbars are implemented in the PySide.QtGui.QToolBar class. You add a toolbar to a main window with addToolBar() .
You control the initial position of toolbars by assigning them to a specific Qt.ToolBarArea . You can split an area by inserting a toolbar break - think of this as a line break in text editing - with addToolBarBreak() or insertToolBarBreak() . You can also restrict placement by the user with QToolBar.setAllowedAreas() and QToolBar.setMovable() .
The size of toolbar icons can be retrieved with iconSize() . The sizes are platform dependent; you can set a fixed size with setIconSize() . You can alter the appearance of all tool buttons in the toolbars with setToolButtonStyle() .
An example of toolbar creation follows:
def createToolBars(self): fileToolBar = addToolBar(tr("File")) fileToolBar.addAction(Act)
Creating Dock Widgets¶
Dock widgets are implemented in the PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget class. A dock widget is a window that can be docked into the main window. You add dock widgets to a main window with addDockWidget() .
There are four dock widget areas as given by the Qt.DockWidgetArea enum: left, right, top, and bottom. You can specify which dock widget area that should occupy the corners where the areas overlap with setCorner() . By default each area can only contain one row (vertical or horizontal) of dock widgets, but if you enable nesting with setDockNestingEnabled() , dock widgets can be added in either direction.
Two dock widgets may also be stacked on top of each other. A PySide.QtGui.QTabBar is then used to select which of the widgets that should be displayed.
We give an example of how to create and add dock widgets to a main window:
dockWidget = QDockWidget(tr("Dock Widget"), self) dockWidget.setAllowedAreas(Qt.LeftDockWidgetArea | Qt.RightDockWidgetArea) dockWidget.setWidget(dockWidgetContents) addDockWidget(Qt.LeftDockWidgetArea, dockWidget)
The Status Bar¶
You can set a status bar with setStatusBar() , but one is created the first time statusBar() (which returns the main window’s status bar) is called. See PySide.QtGui.QStatusBar for information on how to use it.
Storing State¶
PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow can store the state of its layout with saveState() ; it can later be retrieved with restoreState() . It is the position and size (relative to the size of the main window) of the toolbars and dock widgets that are stored.
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMenuBar PySide.QtGui.QToolBar PySide.QtGui.QStatusBar PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget Application Example Dock Widgets Example MDI Example SDI Example Menus Example
- class PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow([parent=None[, flags=0]])¶
Parameters: - flags – PySide.QtCore.Qt.WindowFlags
- parent – PySide.QtGui.QWidget
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.DockOption¶
This enum contains flags that specify the docking behavior of PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow .
Constant Description QMainWindow.AnimatedDocks Identical to the animated() property. QMainWindow.AllowNestedDocks Identical to the dockNestingEnabled() property. QMainWindow.AllowTabbedDocks The user can drop one dock widget “on top” of another. The two widgets are stacked and a tab bar appears for selecting which one is visible. QMainWindow.ForceTabbedDocks Each dock area contains a single stack of tabbed dock widgets. In other words, dock widgets cannot be placed next to each other in a dock area. If this option is set, AllowNestedDocks has no effect. QMainWindow.VerticalTabs The two vertical dock areas on the sides of the main window show their tabs vertically. If this option is not set, all dock areas show their tabs at the bottom. Implies AllowTabbedDocks . See also PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setTabPosition() . These options only control how dock widgets may be dropped in a PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow . They do not re-arrange the dock widgets to conform with the specified options. For this reason they should be set before any dock widgets are added to the main window. Exceptions to this are the AnimatedDocks and VerticalTabs options, which may be set at any time.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addDockWidget(area, dockwidget, orientation)¶
Parameters: - area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea
- dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
- orientation – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Orientation
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addDockWidget(area, dockwidget)
Parameters: - area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea
- dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBar(area, toolbar)¶
Parameters: - area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolBarArea
- toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBar(title)
Parameters: title – unicode Return type: PySide.QtGui.QToolBar This is an overloaded function.
Creates a PySide.QtGui.QToolBar object, setting its window title to title , and inserts it into the top toolbar area.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBar(toolbar)
Parameters: toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar This is an overloaded function.
Equivalent of calling addToolBar( Qt.TopToolBarArea , toolbar )
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBarBreak([area=Qt.TopToolBarArea])¶
Parameters: area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolBarArea
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.centralWidget()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QWidget Returns the central widget for the main window. This function returns zero if the central widget has not been set.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.corner(corner)¶
Parameters: corner – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Corner Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.createPopupMenu()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMenu Returns a popup menu containing checkable entries for the toolbars and dock widgets present in the main window. If there are no toolbars and dock widgets present, this function returns a null pointer.
By default, this function is called by the main window when the user activates a context menu, typically by right-clicking on a toolbar or a dock widget.
If you want to create a custom popup menu, reimplement this function and return a newly-created popup menu. Ownership of the popup menu is transferred to the caller.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.dockOptions()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.DockOptions This property holds the docking behavior of PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow .
The default value is AnimatedDocks | AllowTabbedDocks .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.dockWidgetArea(dockwidget)¶
Parameters: dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea Returns the Qt.DockWidgetArea for dockwidget . If dockwidget has not been added to the main window, this function returns Qt::NoDockWidgetArea .
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addDockWidget() PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.splitDockWidget() Qt.DockWidgetArea
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.documentMode()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar for tabbed dockwidgets is set to document mode..
The default is false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.iconSize()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.QSize This property holds size of toolbar icons in this mainwindow..
The default is the default tool bar icon size of the GUI style. Note that the icons used must be at least of this size as the icons are only scaled down.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.iconSizeChanged(iconSize)¶
Parameters: iconSize – PySide.QtCore.QSize
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.insertToolBar(before, toolbar)¶
Parameters: - before – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar
- toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar
Inserts the toolbar into the area occupied by the before toolbar so that it appears before it. For example, in normal left-to-right layout operation, this means that toolbar will appear to the left of the toolbar specified by before in a horizontal toolbar area.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.insertToolBarBreak(before)¶
Parameters: before – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar Inserts a toolbar break before the toolbar specified by before .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.isAnimated()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether manipulating dock widgets and tool bars is animated.
When a dock widget or tool bar is dragged over the main window, the main window adjusts its contents to indicate where the dock widget or tool bar will be docked if it is dropped. Setting this property causes PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow to move its contents in a smooth animation. Clearing this property causes the contents to snap into their new positions.
By default, this property is set. It may be cleared if the main window contains widgets which are slow at resizing or repainting themselves.
Setting this property is identical to setting the AnimatedDocks option using PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockOptions() .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.isDockNestingEnabled()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether docks can be nested.
If this property is false, dock areas can only contain a single row (horizontal or vertical) of dock widgets. If this property is true, the area occupied by a dock widget can be split in either direction to contain more dock widgets.
Dock nesting is only necessary in applications that contain a lot of dock widgets. It gives the user greater freedom in organizing their main window. However, dock nesting leads to more complex (and less intuitive) behavior when a dock widget is dragged over the main window, since there are more ways in which a dropped dock widget may be placed in the dock area.
Setting this property is identical to setting the AllowNestedDocks option using PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockOptions() .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.isSeparator(pos)¶
Parameters: pos – PySide.QtCore.QPoint Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QMenuBar Returns the menu bar for the main window. This function creates and returns an empty menu bar if the menu bar does not exist.
If you want all windows in a Mac application to share one menu bar, don’t use this function to create it, because the menu bar created here will have this PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow as its parent. Instead, you must create a menu bar that does not have a parent, which you can then share among all the Mac windows. Create a parent-less menu bar this way:
menuBar = QMenuBar()
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QWidget Returns the menu bar for the main window. This function returns null if a menu bar hasn’t been constructed yet.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.removeDockWidget(dockwidget)¶
Parameters: dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget Removes the dockwidget from the main window layout and hides it. Note that the dockwidget is not deleted.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.removeToolBar(toolbar)¶
Parameters: toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar Removes the toolbar from the main window layout and hides it. Note that the toolbar is not deleted.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.removeToolBarBreak(before)¶
Parameters: before – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar Removes a toolbar break previously inserted before the toolbar specified by before .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.restoreDockWidget(dockwidget)¶
Parameters: dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Restores the state of dockwidget if it is created after the call to PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.restoreState() . Returns true if the state was restored; otherwise returns false.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.restoreState(state[, version=0])¶
Parameters: - state – PySide.QtCore.QByteArray
- version – PySide.QtCore.int
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool
Restores the state of this mainwindow’s toolbars and dockwidgets. The version number is compared with that stored in state . If they do not match, the mainwindow’s state is left unchanged, and this function returns false ; otherwise, the state is restored, and this function returns true .
To restore geometry saved using PySide.QtCore.QSettings , you can use code like this:
def readSettings(self): settings = QSettings("MyCompany", "MyApp") restoreGeometry(settings.value("myWidget/geometry")) restoreState(settings.value("myWidget/windowState"))
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.saveState([version=0])¶
Parameters: version – PySide.QtCore.int Return type: PySide.QtCore.QByteArray Saves the current state of this mainwindow’s toolbars and dockwidgets. The version number is stored as part of the data.
The PySide.QtCore.QObject.objectName() property is used to identify each PySide.QtGui.QToolBar and PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget . You should make sure that this property is unique for each PySide.QtGui.QToolBar and PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget you add to the PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow
To restore the saved state, pass the return value and version number to PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.restoreState() .
To save the geometry when the window closes, you can implement a close event like this:
def closeEvent(self, event): settings = QSettings("MyCompany", "MyApp") settings.setValue("geometry", self.saveGeometry()) settings.setValue("windowState", self.saveState()) QMainWindow.closeEvent(self, event)
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setAnimated(enabled)¶
Parameters: enabled – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether manipulating dock widgets and tool bars is animated.
When a dock widget or tool bar is dragged over the main window, the main window adjusts its contents to indicate where the dock widget or tool bar will be docked if it is dropped. Setting this property causes PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow to move its contents in a smooth animation. Clearing this property causes the contents to snap into their new positions.
By default, this property is set. It may be cleared if the main window contains widgets which are slow at resizing or repainting themselves.
Setting this property is identical to setting the AnimatedDocks option using PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockOptions() .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setCentralWidget(widget)¶
Parameters: widget – PySide.QtGui.QWidget Sets the given widget to be the main window’s central widget.
Note: PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow takes ownership of the widget pointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setCorner(corner, area)¶
Parameters: - corner – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Corner
- area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockNestingEnabled(enabled)¶
Parameters: enabled – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether docks can be nested.
If this property is false, dock areas can only contain a single row (horizontal or vertical) of dock widgets. If this property is true, the area occupied by a dock widget can be split in either direction to contain more dock widgets.
Dock nesting is only necessary in applications that contain a lot of dock widgets. It gives the user greater freedom in organizing their main window. However, dock nesting leads to more complex (and less intuitive) behavior when a dock widget is dragged over the main window, since there are more ways in which a dropped dock widget may be placed in the dock area.
Setting this property is identical to setting the AllowNestedDocks option using PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockOptions() .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDockOptions(options)¶
Parameters: options – PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.DockOptions This property holds the docking behavior of PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow .
The default value is AnimatedDocks | AllowTabbedDocks .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setDocumentMode(enabled)¶
Parameters: enabled – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the tab bar for tabbed dockwidgets is set to document mode..
The default is false.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setIconSize(iconSize)¶
Parameters: iconSize – PySide.QtCore.QSize This property holds size of toolbar icons in this mainwindow..
The default is the default tool bar icon size of the GUI style. Note that the icons used must be at least of this size as the icons are only scaled down.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setMenuBar(menubar)¶
Parameters: menubar – PySide.QtGui.QMenuBar Sets the menu bar for the main window to menuBar .
Note: PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow takes ownership of the menuBar pointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setMenuWidget(menubar)¶
Parameters: menubar – PySide.QtGui.QWidget Sets the menu bar for the main window to menuBar .
PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow takes ownership of the menuBar pointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setStatusBar(statusbar)¶
Parameters: statusbar – PySide.QtGui.QStatusBar Sets the status bar for the main window to statusbar .
Setting the status bar to 0 will remove it from the main window. Note that PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow takes ownership of the statusbar pointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.
See also
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setTabPosition(areas, tabPosition)¶
Parameters: - areas – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetAreas
- tabPosition – PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabPosition
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setTabShape(tabShape)¶
Parameters: tabShape – PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabShape This property holds the tab shape used for tabbed dock widgets..
The default is QTabWidget.Rounded .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setToolButtonStyle(toolButtonStyle)¶
Parameters: toolButtonStyle – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolButtonStyle This property holds style of toolbar buttons in this mainwindow..
The default is Qt.ToolButtonIconOnly .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.setUnifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac(set)¶
Parameters: set – PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the window uses the unified title and toolbar look on Mac OS X.
This property is false by default and only has any effect on Mac OS X 10.4 or higher.
If set to true, then the top toolbar area is replaced with a Carbon HIToolbar or a Cocoa NSToolbar (depending on whether Qt was built with Carbon or Cocoa). All toolbars in the top toolbar area and any toolbars added afterwards are moved to that. This means a couple of things.
- QToolBars in this toolbar area are not movable and you cannot drag other toolbars to it
- Toolbar breaks are not respected or preserved
- Any custom widgets in the toolbar will not be shown if the toolbar becomes too small (only actions will be shown)
- Before Qt 4.5, if you called PySide.QtGui.QWidget.showFullScreen() on the main window, the QToolbar would disappear since it is considered to be part of the title bar. Qt 4.5 and up will now work around this by pulling the toolbars out and back into the regular toolbar and vice versa when you swap out.
Setting this back to false will remove these restrictions.
The Qt.WA_MacBrushedMetal attribute takes precedence over this property.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.splitDockWidget(after, dockwidget, orientation)¶
Parameters: - after – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
- dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
- orientation – PySide.QtCore.Qt.Orientation
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.statusBar()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QStatusBar Returns the status bar for the main window. This function creates and returns an empty status bar if the status bar does not exist.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.tabPosition(area)¶
Parameters: area – PySide.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabPosition
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.tabShape()¶
Return type: PySide.QtGui.QTabWidget.TabShape This property holds the tab shape used for tabbed dock widgets..
The default is QTabWidget.Rounded .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.tabifiedDockWidgets(dockwidget)¶
Parameters: dockwidget – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget Return type: Returns the dock widgets that are tabified together with dockwidget .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.tabifyDockWidget(first, second)¶
Parameters: - first – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
- second – PySide.QtGui.QDockWidget
Moves second dock widget on top of first dock widget, creating a tabbed docked area in the main window.
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.toolBarArea(toolbar)¶
Parameters: toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolBarArea Returns the Qt.ToolBarArea for toolbar . If toolbar has not been added to the main window, this function returns Qt::NoToolBarArea .
See also
PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBar() PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.addToolBarBreak() Qt.ToolBarArea
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.toolBarBreak(toolbar)¶
Parameters: toolbar – PySide.QtGui.QToolBar Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool Returns whether there is a toolbar break before the toolbar .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.toolButtonStyle()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolButtonStyle This property holds style of toolbar buttons in this mainwindow..
The default is Qt.ToolButtonIconOnly .
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.toolButtonStyleChanged(toolButtonStyle)¶
Parameters: toolButtonStyle – PySide.QtCore.Qt.ToolButtonStyle
- PySide.QtGui.QMainWindow.unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac()¶
Return type: PySide.QtCore.bool This property holds whether the window uses the unified title and toolbar look on Mac OS X.
This property is false by default and only has any effect on Mac OS X 10.4 or higher.
If set to true, then the top toolbar area is replaced with a Carbon HIToolbar or a Cocoa NSToolbar (depending on whether Qt was built with Carbon or Cocoa). All toolbars in the top toolbar area and any toolbars added afterwards are moved to that. This means a couple of things.
- QToolBars in this toolbar area are not movable and you cannot drag other toolbars to it
- Toolbar breaks are not respected or preserved
- Any custom widgets in the toolbar will not be shown if the toolbar becomes too small (only actions will be shown)
- Before Qt 4.5, if you called PySide.QtGui.QWidget.showFullScreen() on the main window, the QToolbar would disappear since it is considered to be part of the title bar. Qt 4.5 and up will now work around this by pulling the toolbars out and back into the regular toolbar and vice versa when you swap out.
Setting this back to false will remove these restrictions.
The Qt.WA_MacBrushedMetal attribute takes precedence over this property.




